GYNECOLOGY
Annual and Well Woman Exams
Most sexually active women should have a yearly gynecological exam. At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology, we see this visit as the perfect time to discuss general health concerns and family planning options. Other commonly discussed topics during your annual examination with us may be prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases, screening for cancer, vaccinations, obesity, and genetic cancer screening with consideration of family history. This is also the time when other gynecological concerns such as menstrual irregularities and urinary incontinence may be brought to light and addressed.
Cervical Cancer Screening
Most sexually active women should have cervical cancer screening beginning at the age of 21. Not every woman needs a pap smear every year. Depending on your history, the pap smear or cervical cancer screening may be performed at different intervals in different age groups. Having your pap smear done on time and as recommended by your doctor is the best preventative measure for cervical cancer.
Breast Cancer Risk Assessment and Screening
There are many tools available to assess a patient’s risk of breast cancer. Some risk factors for breast cancer you can change are physical inactivity, obesity, and alcohol intake. Some risk factors that you cannot change are advancing age, family history of breast or ovarian cancer, a personal history of breast masses, and a family history of specific mutations that are known to lead to breast cancer. At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology, our laboratory has the capability of testing for these mutations. Important preventative and screening measures are mammograms, breast ultrasounds, and magnetic resonance imaging. We work closely with our radiology partners to expedite these studies for you whenever needed.
Menopause
Menopause occurs when your body loses the hormonal support of the estrogen produced in the ovaries. This may occur naturally or surgically. The consequences of the loss of estrogen can be severe and long-lasting. Some common symptoms are hot flashes, insomnia, mood swings, vaginal dryness, and pain during intercourse. Some non-medical options for treatment include behavioral and lifestyle modifications. Medical treatments include natural medications as well as synthetic hormonal and non-hormonal options. Bone density is lost rapidly in the post-menopausal years. Screening with bone density scans and appropriate treatment is important. If you are experiencing symptoms of menopause, come see us at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology. Together we can explore the best treatment option for you.
Infertility
Infertility may affect up to 15% of couples. Although a significant number of cases of infertility remain unexplained, there are several factors that can affect your ability to achieve a pregnancy. Older patients should be promptly evaluated. Some important factors to consider are chronic and pre-existing disorders, ovulatory dysfunction (irregular periods), and diminished ovarian reserve or the number of oocytes (eggs) available for fertilization at any given point in time. Structural abnormalities in your reproductive tract can also affect your ability to get pregnant and imaging studies may be necessary. Male partners may be responsible for 40-50% of infertility cases and an analysis of their sperm may be needed. At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology, we work closely with other infertility specialists who may offer you assisted reproductive technology such as in-vitro fertilization and artificial insemination.

Irregular/Painful Menses
If your period does not happen on time, it happens too often, it is too heavy, if you notice a sudden change in its pattern, or if your periods are too painful, an evaluation may be warranted. Several undiagnosed medical conditions may lead to a change in your menstrual pattern including hormonal disorders and metabolic disorders like diabetes mellitus. In addition, changes in the anatomy of your reproductive tract often lead to changes in your menstrual pattern and pain levels. Imaging studies such as a pelvic ultrasound may help in diagnosing these conditions. At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology, we offer every medical and surgical option to help you with an irregular menstrual pattern.
Heavy Menses
Heavy periods are among the most common afflictions in reproductive-age women. Normal physiologic changes, hormone imbalances, benign and malignant tumors as well as infections are some common causes. At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology, we have a wide array of diagnostic and medical treatment modalities available. Inpatient surgical management may also be an option. Come see us for a thorough evaluation and a discussion of the best treatment plan for you.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases disproportionately affect women. Young women ages 15-24 consistently have the highest rates of infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea. These infections may have long-term sequelae such as pelvic pain and infertility and they must be treated as soon as they are diagnosed. At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology we can routinely perform a screening for STDs at the time of an annual exam, or you may request one at any time. Though many infections are asymptomatic, some common symptoms are vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, and irregular/heavy periods.
Family Planning and Contraception
At Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology, we can help you prevent an unplanned pregnancy. There are a variety of options, all of which are available in our clinic. Some methods contain hormones and some do not. Your medical history can determine if you should avoid a specific form of birth control. You may also decide that permanent sterilization is the best option for you.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a condition that leads to unintentional loss of urine. The two primary types of incontinence are urge urinary incontinence (more commonly known as overactive bladder) and stress urinary incontinence. An overactive bladder leads to a sudden urge to urinate with accidents upon trying to reach the bathroom or bedwetting. Lifestyle modifications and changes in diet may help. Medications can also be helpful. Stress urinary incontinence leads to loss of urine with increased pressure during coughing, sneezing, or heavy lifting. It may be treated with lifestyle modifications, weight loss, and certain exercises. Surgery may be an option.
Chronic Pelvic Pain
Chronic pelvic pain is pain below your belly button and between your hips that lasts longer than six months. It can be caused by several conditions or be a symptom of a disease. In many instances, it may not be possible to determine the cause. Come see your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology if your symptoms are worsening or affecting your daily life. Your history and physical exam will guide the evaluation you will need.
Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual Dysfunction is a condition that prevents you from wanting or enjoying sexual activity. While it can happen at any stage in life, it is more common with increasing age. Some common causes are physical trauma, psychological issues, drugs, alcohol, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain medications. After a thorough history and physical examination, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology will suggest the best treatment option for you. Medications may help.
In-Office Surgeries and Procedures

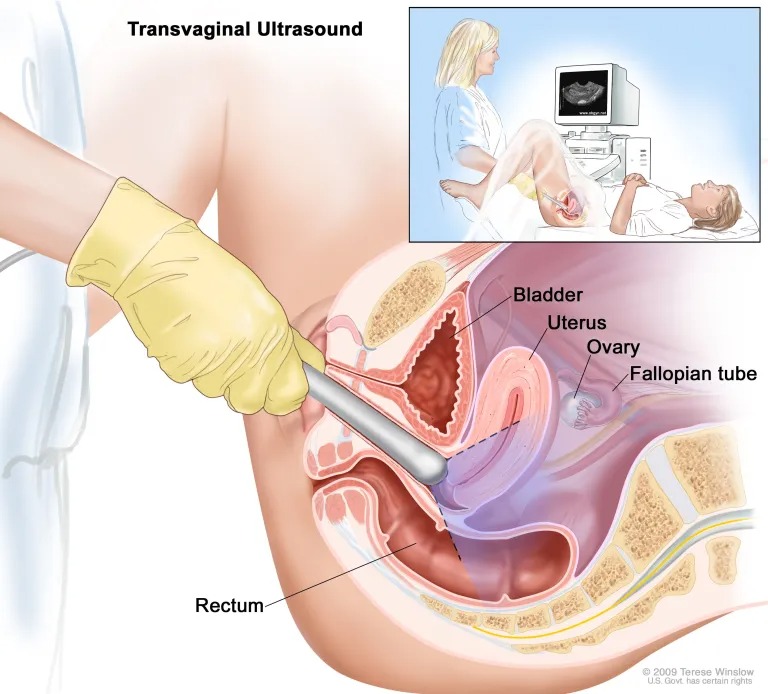
Pelvic and Transvaginal Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is a highly flexible technology for pregnancy and gynecological concerns. With the on-site ultrasounds at Puig Obstetrics & Gynecology, you can get the information you need to plan and make informed decisions about your health. Same-day ultrasounds are always available. Book your appointment by calling the office today.
How does an ultrasound work?
During your ultrasound, you lie on the exam table in a comfortable position, just as with a regular pelvic exam.
Transvaginal ultrasound
In a transvaginal ultrasound, your Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology care provider gently inserts an ultrasound wand into your vaginal canal. The sound waves generate images of your reproductive organs and surrounding structures for your provider to examine.
Ultrasounds are quick and painless. Same-day ultrasounds are available at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology for your convenience.
When is ultrasound used for gynecological concerns?
Your Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology provider might use ultrasound imaging as a diagnostic tool. Ultrasounds allow your care provider to see the inner workings of your reproductive system including your uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix, in detail.
If you’re having problems such as pelvic pain, ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, infertility, or abnormal menstrual bleeding, your provider may use an ultrasound to make a diagnosis. Sometimes, ultrasound is also part of the treatment for gynecological problems.
Vulvar and Skin Biopsies
Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology and you may decide together that an abnormal area in your skin needs to be sampled. This is done under local anesthesia. The tissue is sent to a laboratory for examination.

Excision of Skin Lesions
Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology and you may decide together that excising an entire lesion may be the best treatment option. The tissue is sent to a laboratory for examination.

Incision and Drainage Procedures
Most incision and drainage procedures are performed for abscesses or infections that develop on the most superficial layer of the skin. Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may recommend incising the skin and draining the pus from the abscess cavity.
This typically relieves your pain immediately. Antibiotic treatment may be warranted.

Colposcopy and Cervical Biopsies
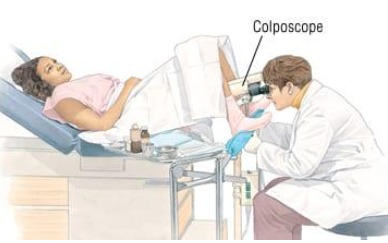
What is a colposcopy?
If you have an abnormal pap smear, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may recommend a colposcopy. A colposcopy is a procedure to look at the cervix through a special magnifying device called a colposcope. It shines a light onto the vagina and the cervix. During a colposcopy, we may see abnormal areas. Biopsies may be taken and sent to a laboratory for testing.
Why is colposcopy done?
A colposcopy will allow us to examine your cervix, vagina, or vulvar skin with magnification so that areas of abnormal cell growth can be identified. The purpose of the biopsy is to remove a small piece of tissue for microscopic examination by a pathologist. A biopsy is the most reliable way to obtain an accurate evaluation of abnormal tissue.
What are the risks of colposcopy?
Infection and bleeding are the primary risks with this procedure, though both are highly uncommon. During the procedure, you may feel cramping or have some minor discomfort. You may also experience light bleeding or spotting a few days after the biopsy.
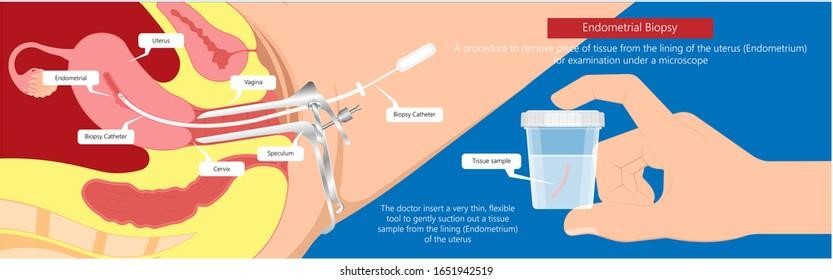
Endometrial (uterine) Biopsies
What is an endometrial biopsy?
If you are experiencing abnormal uterine bleeding, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may perform an endometrial biopsy to investigate the cause of the bleeding. During an endometrial biopsy, tissue samples are taken from the inside of the uterus, using a thin, hollow catheter.
Because this procedure can cause momentary cramping, we suggest you take ibuprofen (with food) one hour before your exam. Fortunately, the cramping is often short-lived and subsides quickly.
It is important to note that your period may be heavier than usual following the procedure. Also, you should not douche or engage in intercourse for five days following the biopsy. Bathing and showering are permissible.
LEEP (loop electro-excisional procedure) Surgical Procedures for the Management of Precancerous Lesions on the Cervix.
What is a LEEP (loop electro-excisional procedure) procedure?
LEEP is an acronym for “loop electrosurgical excision procedure.” This procedure is often recommended after abnormal pap test results have been confirmed by colposcopy.
During LEEP, abnormal cells are cut away from the cervix using a thin wire loop through which an electrical current is passed. The biopsied tissue is then sent to a pathologist for review. Typically, you will receive pathology results within seven to fourteen office days
Before LEEP, it is recommended that you take ibuprofen (with food) one hour before your scheduled exam. The ibuprofen will help with the mild cramping that may follow the procedure. Additionally, for your comfort during the procedure, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology will place a local anesthetic.
While recovery depends upon the extent of the procedure, typically, women return to light to normal activities within one to three days. It is important that you avoid intercourse, douching, tampons, and strenuous activities for four weeks following LEEP.


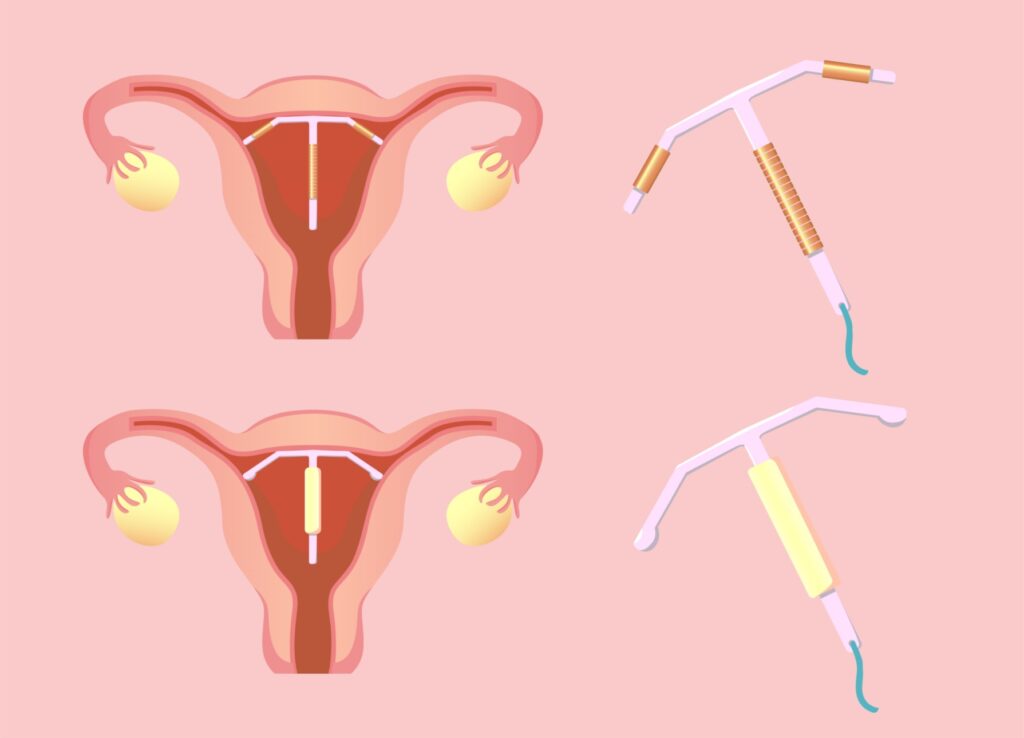
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Placement
An intrauterine device also called an IUD, is a very small, plastic or metal flexible device that is shaped like a T. It also has a string attached to the end of it. (The string hangs out of the cervix so that you can check every once in a while, to make sure the IUD is still in place.)
During an office visit, your Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology provider will place the IUD inside your uterus to prevent pregnancy or to control abnormal uterine bleeding. The IUD will remain in your uterus until it is removed by your doctor.
The IUD works to prevent the sperm from joining the egg. There are several types of IUDs available in the United States and it is recommended that you talk with your Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology provider to determine which type is best for you.
Depending upon the type of IUD chosen, pregnancy can be prevented for up to 3 to 10 years. Some IUDs have hormones while others do not.
For many, the IUD is a good choice because it is effective, convenient, and inexpensive. Please talk with your Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology provider to discuss any health risks involved and to determine if you are a good candidate for an IUD.
Dispelling IUD Myths
One of the greatest hurdles facing IUD use is that many people have been led to believe inaccurate information about it, such as:
- You can’t use an IUD if you have not given birth
- Teenagers cannot use IUDs.
- IUDs cause infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease
- IUDs are not safe
Before an IUD insertion, it is important to first dispel these myths to alleviate any worries and feel more confident during insertion.


Etonogestrel Implant (Nexplanon) Placement
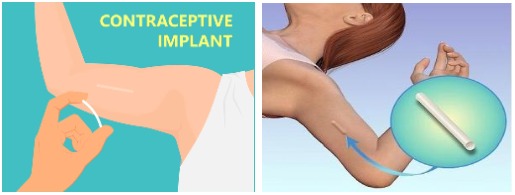
What is the birth control implant (Nexplanon)?
The birth control implant is a flexible, plastic rod about the size of a matchstick that is inserted just under the skin in the inner upper arm. It releases a hormone into the body. The implant is approved for up to 3 years of use. The brand name is Nexplanon and it was previously known as Implanon.
How does the birth control implant work?
The hormone in the implant prevents pregnancy mainly by stopping ovulation. The hormone in the implant also thickens the mucus of the cervix. This makes it harder for sperm to enter the uterus and reach the egg. The hormone also thins the lining of the uterus.
What are the benefits of the birth control implant?
The implant has the following benefits:
- It is easy to use. Once it is in place, you do not have to do anything else to prevent pregnancy.
- No one can tell that you are using birth control. The implant cannot be seen under the skin (but it can be felt).
- It can be inserted immediately after a miscarriage or childbirth, and while breastfeeding.
- It does not interfere with sex or daily activities.
- Almost all women can use the implant. Few medical conditions prevent its use.
- It reduces pain during your menstrual period.
- If you wish to get pregnant, or if you want to stop using it, you can simply have the implant removed.
How is the birth control implant inserted?
Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology will insert the implant into your arm. Your provider will numb a small area on the inside of your upper arm with local pain medicine. The implant is placed under the skin with a special inserter. The procedure takes only a few minutes.
How is the birth control implant removed?
When you are ready to stop using the implant, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology will remove it. A small area on your upper arm is numbed with a local anesthetic. One small incision is made. The implant is removed through a small incision. The procedure usually takes only a few minutes.
What are the possible side effects of using the birth control implant?
Like IUDs, the implant can cause changes in menstrual bleeding. The most common change is unpredictable bleeding. Menstrual periods may be less frequent and may stop completely. For some women, periods may be more frequent or last longer. Other side effects may include digestive difficulties, headaches, breast pain, weight gain, and acne.
What are the possible risks of using the birth control implant?
Possible risks with the use of the implant include the following:
- Problems with insertion or removal of the implant. These problems are rare.
- Although rare, if a woman gets pregnant while the implant is inserted, there is a slightly increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. The implant should be removed if pregnancy occurs.
Marsupialization Procedures
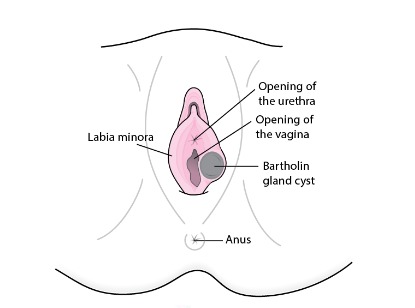
What is a marsupialization procedure?
Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may recommend and perform a marsupialization which is a surgical procedure that removes cysts in a way that makes them less likely to return. Once the cyst has been opened and drained, the edges are sutured together to form a permanent opening that allows fluid to drain easily. A marsupialization procedure is typically performed on a Bartholin’s gland cyst/abscess. Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology will administer a local anesthetic before the incision and drainage portion of the procedure.
What is a Bartholin’s gland cyst/abscess?
A fluid-filled swelling (cyst) in the Bartholin’s glands lubricates the vagina.
Bartholin’s cysts are common. Fluid may accumulate when the opening of the Bartholin’s gland becomes obstructed due to an infection or injury.
A small, noninfected Bartholin’s cyst may not be noticeable unless it grows. If the cyst becomes infected, symptoms may include pain and discomfort.
Often, treatment may be needed in the form of warm sitz baths, anti-inflammatories, and surgical drainage. Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may recommend a marsupialization procedure.

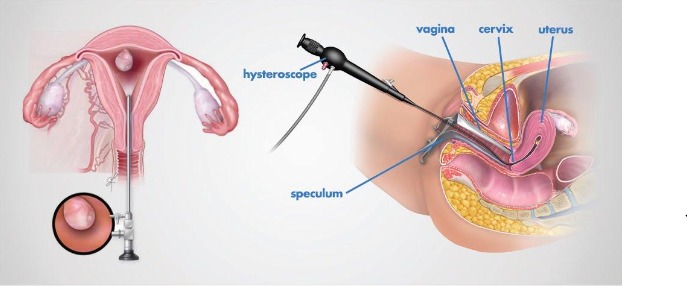
Diagnostic and Operative Hysteroscopy
What is hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is used to diagnose or treat problems in the uterus. A hysteroscope is a thin, lighted camera. It is inserted through your vagina into your uterus. The hysteroscope transmits the image of your uterus onto a screen. Other instruments are used along with the hysteroscope for treatment.
Why is hysteroscopy done?
Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may recommend a hysteroscopy to find the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding. Abnormal bleeding can mean that a woman’s menstrual periods are heavier or longer than usual or occur less often or more often than normal. Bleeding between menstrual periods also is abnormal.
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
During a diagnostic hysteroscopy, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may evaluate the causes of abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, infertility, and/or other complaints.
Operative Hysteroscopy (Removal of Polyps and/or Fibroids)
During operative hysteroscopy, your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may evaluate and treat causes of abnormal uterine bleeding, infertility, and repeated miscarriages. Small polyps may be excised in the office setting and foreign objects, such as retained intrauterine devices (IUDs), may be removed.


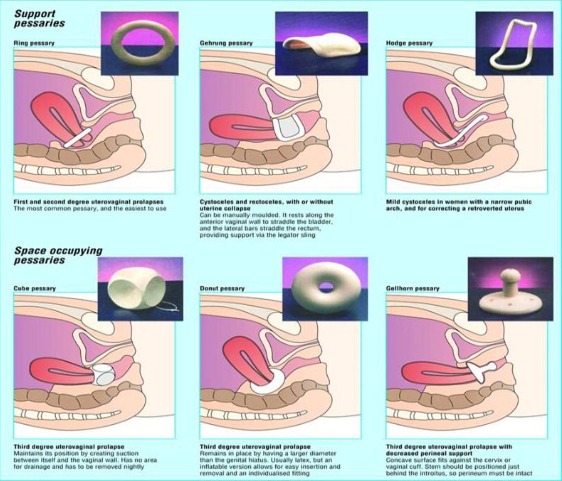
Pessary Fitting
Often the first treatment option for vaginal prolapse may be a pessary which is a plastic/rubber device that fits tightly into the vaginal canal recreating the support system and correcting the prolapse. Your provider at Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology may make an appointment in our facility for a pessary fitting if this is the best option for you.
Urodynamics and Cystometrogram
What is it?
Urodynamics is the primary diagnostic procedure for the investigation of the function and dysfunction of the lower urinary tract.
A cystometrogram allows us to assess how your bladder and sphincter behave while you store urine and when you pass urine. This test is done for people with urinary incontinence, people who have difficulty with urination, and in people with neurologic diseases that can affect bladder function. This test will measure your bladder capacity and pressure. By doing this we can identify problems such as an overactive bladder.
Who needs Urodynamics/Cystometrogram?
If you are experiencing urinary stress incontinence or other bladder issues such as urinary frequency and urgency, your Puig Obstetrics and Gynecology provider may suggest urodynamics testing and a cystometrogram (CMG).
What to Expect
This test will take about 15-20 minutes. You will be positioned on an exam table lying on your back. You will first be asked to void into the collection container, as the machine measures your voiding pressure. Your urethral opening will then be cleansed with betadine to eliminate any bacteria on the surface. A lubricated catheter with sensors will be inserted into your urethra and advanced into the bladder. With the bladder catheter in place, we will then check to see if there is residual urine in your bladder after voiding.
The bladder will then be filled with saline solution and filling pressures recorded. We will ask you remain very still, and to report any sensations that you might have such as coolness from the saline fluid, fullness, the need to urinate, urgency, pain, bladder spasms, etc. You may experience some urine leakage during the study. Don’t be embarrassed because this should be expected.
You may experience a sense of burning or pressure when the catheter is inserted into the urethra. It is normal to have some irritation when you urinate for 24-48 hours after the study. You may also note a small amount of blood in the urine.
If you have urinary incontinence, we may tilt the table upright and ask you to cough and then strain. These maneuvers are performed to try to make you leak urine. We will attempt to replicate the urinary symptoms that you experience in your everyday life. If you have urinary retention, we will ask you to try to urinate. Measuring the bladder and urethral pressures, observing sphincter activity, and watching the movements of your bladder and urethra during leakage and urination will help us identify problems so that we can recommend treatment options.
How to prepare for Urodynamics/CMG
1) You may eat, drink, and take your usual medications on the day of your testing. If you have a morning test, it is best if you eat your morning meal before you come in.
2) The testing will not require sedation therefore you will be able to drive yourself home if there is no one to accompany you to the visit.
3) Come to the clinic area with a normally full bladder.
Important information to give to your health care provider prior to testing:
1) Notify your provider if you feel that you have a urinary tract infection—fever, chills, burning with urination, blood in your urine. We will check a urine specimen at some point during your visit but we ask that you inform us if you think you have an active infection.
2) Notify your provider of any drug allergies or allergy to latex, iodine, or shellfish.
3) Notify your provider if you are pregnant or think you are pregnant.

Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy and Biofeedback
You may be a candidate for therapy if:
- You leak urine when you cough, sneeze, exercise, or lift something?
- You leak urine when you feel a strong urge to go but cannot get there in time?
- You have to urinate frequently during the day or get up several times each night?
- You have an uncomfortable feeling of bulging, dropping, or pressure in your vagina?
- You notice any decrease in vaginal sensation?
The average bladder capacity is 10 to 20 ounces although this decreases some with age. Generally, a bladder should empty every 3 to 6 hours, or 4 to 6 times in 24 hours. It is not normal to need to hurry to the toilet if you have normal bladder function.
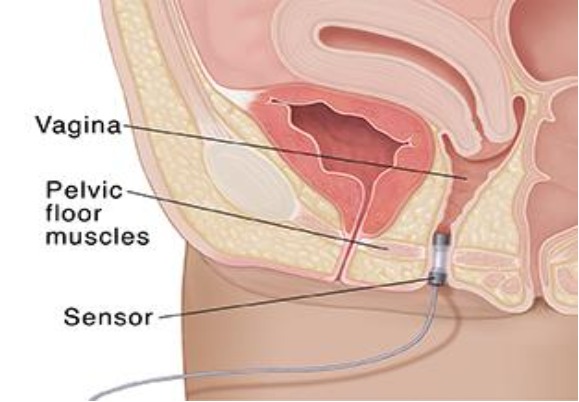
The pelvic floor muscles (PFM) are at the bottom of the pelvis and are shaped like a sling. The muscles support the bladder and form the sphincter surrounding the urethra that controls urination. The muscles may lose strength or become damaged due to childbirth, surgery, aging, illness, or deconditioning.
Physical floor therapy helps with muscle reconditioning. We help patients develop an individualized program for improving the function and strength of the pelvic floor. Pelvic floor exercises can help strengthen these muscles and thus help control urinary problems. Electrical stimulation may also be utilized to strengthen and improve the function of the pelvic floor. Our equipment performs both biofeedback and electrical stimulation and measures which muscles are contracting during pelvic floor rehab exercises. We utilize this information to stimulate areas of weakness. It is also useful for treating fecal incontinence, mild pelvic descent, irritative voiding, some pelvic pain, and some sexual dysfunction.
Patients must participate in and comply with the exercises, behavior changes, and treatments. A vaginal/rectal EMG sensor measures the electrical activity of the muscles during relaxation and contraction. After the initial assessment (approximately one hour), patients are assigned daily exercises to be performed at specific intervals. Initial evaluation is normally followed by three to four weekly visits (30 to 45 minutes each) and subsequent follow-up. Progressive scheduling is likely to result in better outcomes when treatment is completed. The scheduling is dependent on the results of therapy, the patient’s motivation, compliance, and severity of pelvic floor dysfunction.